3D/4D Ultrasound


What to do when and why ?
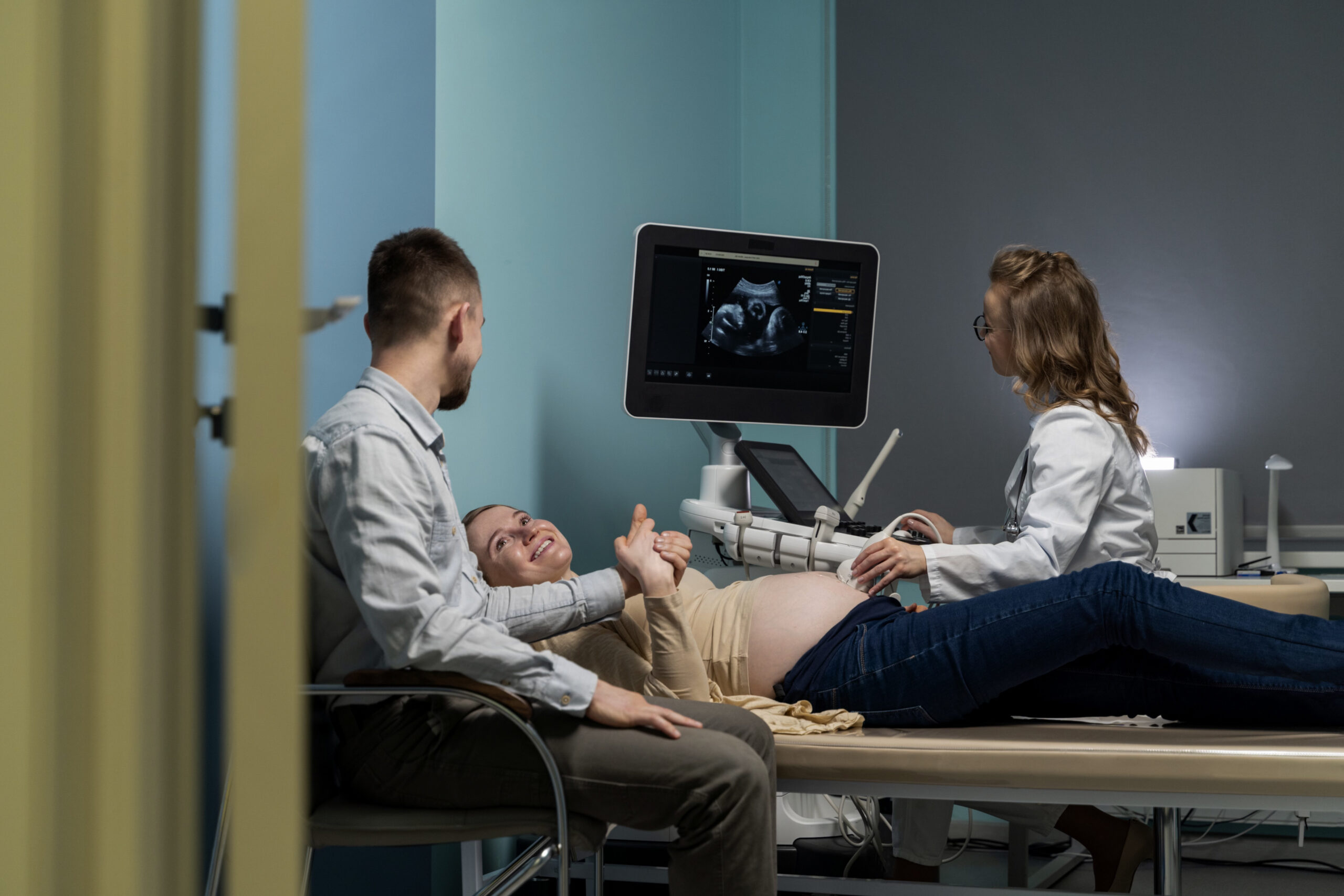
Ideal schedule of pregnancy scans
Monitoring your pregnancy with timely scans ensures both your health and your baby’s well-being. Each scan is designed to check the healthy...

Dating scan – 6 – 8 weeks
This is the first scan of pregnancy.The aim of this scan is to establish
- Location of the Gestation.
That is to look for...

Level I Scan - NT/NB scan – 11- 14 weeks
NT stands for nuchal translucency. NB stands for nasal bone.Somehow for a layman seems pretty weird looking specifically for the nasal bone...

Level 2 anomaly scan - TIFFA- CMF - 18 – 22 weeks
The TIFFA (Targeted Imaging for Fetal Anomalies) Scan, also known as the Level 2 Anomaly Scan, is a detailed ultrasound...

Fetal ECHO – 22- 24 weeks
A Fetal Echocardiography, which is mostly known as Fetal Echo, is an ultrasound performed between 22 and 24 weeks of pregnancy...

Interval Growth Scan
An interval growth scan is an ultrasound performed after 28 weeks of pregnancy, or in the second or third trimester. It is performed...

3D/4D/5D scan – 26 – 28 weeks
3D technology uses an added dimension to a usual 2D images for better visualisation and life like pictures of your baby...

Fetal Dopplers – 28- 36 weeks (as required)
Dopplers are a way of assessing the blood flow. This exam is crucial for timing the delivery.In fetal Dopplers...

Biophysical profile - After 28 weeks as required
A Biophysical Profile (BPP) is an advanced test that is performed after 28 weeks of pregnancy to evaluate the overall well-being of your baby...
Other available pregnancy scans

Early level II anomaly scan – 16 weeks (in case of high risk on NT/NB scan + Dual marker)
This is without question the most important scan of the entire pregnancy. This is when the baby is best visualised...

Chorionic villi sampling – 12- 14 weeks
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) is a prenatal diagnostic test usually performed between 12 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. It usually involves collecting a small sample...

Amniocentesis (invasive) - 16 weeks
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test usually performed around 16 weeks of pregnancy.
It involves withdrawing a small amount of amniotic fluid from...

NIPT - after 12 weeks
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) is a safe, advanced blood test that is performed after 12 weeks of pregnancy. It analyzes fetal DNA circulating in the mother’s blood to assess the risk...

